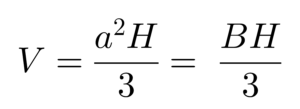Pyramid
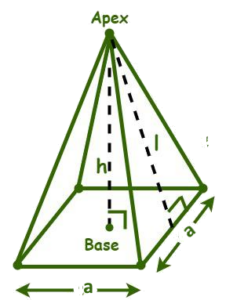
The pyramid is a three-dimensional figure with several flat faces that consists of:
- Base: A simple polygon located at the bottom of the pyramid. It can be a triangle, square, pentagon or any other polygon with straight sides. Depending on the base, they can be regular pyramids (the sides of the base polygon have the same length) or irregular pyramids (the sides of the base polygon have different lengths).
- Lateral faces: Triangles that join the base on one of its sides. The number of lateral faces is equal to the number of sides of the base.
- Vertex: The upper point where all the vertices (corners) of the lateral faces meet.
Examples of pyramids in the real world:
- The pyramids of Egypt are a famous example of regular quadrangular pyramids.
- Space Rockets: Some rocket designs have a shape similar to a pyramid.

Volume formulas
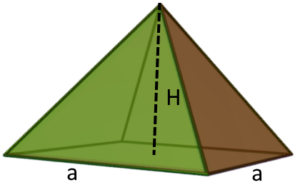
Square pyramid |
 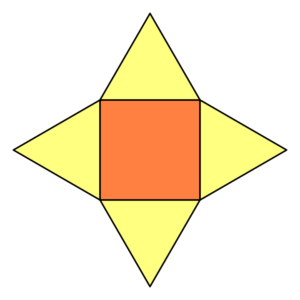 |
Volume of a pyramid is equal to one-third of the area of its base multiplied by its heigh
|
a – lenght base sideH – perpendicular height, height of the pyramidB – area of pyramid base |
Pyramid |
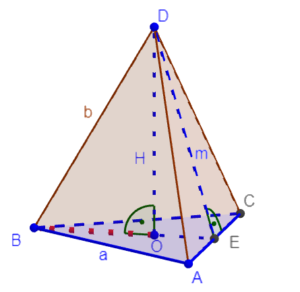 |
H – perpendicular height, height of the pyramidB – area of pyramid basea – lenght base side |
Surface area formulas
Square pyramid |
 
|
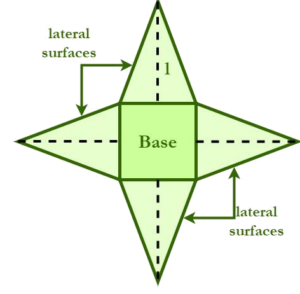
SA= LSA + B A = B + 1/2 x P x l P = 4a LSA =1/2 x P x l= = 1/2 x 4a x l =2al B = a2 Lateral surface area of a pyramid (LSA) = Sum of areas of the lateral surfaces of the pyramid |
SA – surface areaLSA – lateral surface area B – bases area a -base´s side lenghtH – perpendicular height, height of the pyramidB – area of pyramid baseP – perimeter of the base l – slant length of the lateral sides (lenght base to vertex, apex) |
Triangular Pyramid |
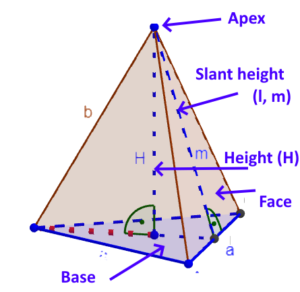 |
SA= LSA + B SA = B + 1/2 x P x l LSA =1/2 x P x l Bases area = polygon area Lateral surface area of a pyramid (LSA) = Sum of areas of the lateral surfaces (triangles) of the pyramid |
SA – surface areaLSA – lateral surface area B – bases area P – base perimeter H – perpendicular height, height of the pyramida -base´s side lenghtl (m) – slant length of the lateral sides. Bases area = polygon area h – height of the triangle |