Commutative law
The definition of commutative law states that when we add or multiply two numbers then the resultant value remains the same, even if we change the position of the two numbers.
It means that you can swap numbers around and still get the same answer when you add or when you multiply.
Examples:
Addition |
Multiplication |
| a + b = b + a | a * b = b * a or ab =ba |
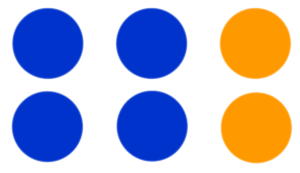 |
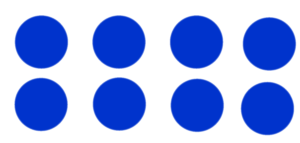 |
|
4 + 2 = 2 + 4 4 + 2 = 6 and 2 + 4 = 6 |
4 * 2 = 2 * 4 4 * 2 = 8 and 2 * 4 = 8 |
Prashanthi Rao , LicenseCC-BY-SA, GeoGebra Terms of Use
Linda Fahlberg-Stojanovska, LicenseCC-BY-SA, GeoGebra Terms of Use
Linda Fahlberg-Stojanovska , LicenseCC-BY-SA, GeoGebra Terms of Use
