Trapezium, trapezoid
A trapezium (UK) or a trapezoid (US)
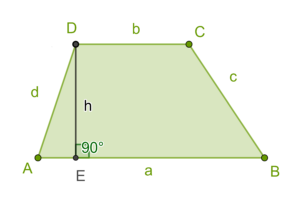
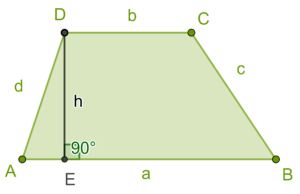
A trapezium is a quadrilateral having two parallel sides of unequal length and the other two sides are non-parallel. The parallel sides of a trapezium are called bases (AD and DC or a and b) and the non-parallel sides of a trapezium are called legs (AD and BC or c and d).
If the legs are equal in length, the trapezoid is called isosceles.
The distance between the bases is called the altitudes of the trapezoid (DE).
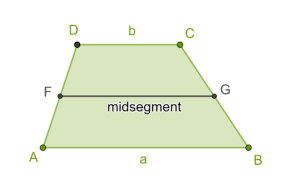
The midsegment (FG) of a trapezoid is the segment connecting the midpoints of the two non-parallel sides (AF=FD and BG=GC).
A trapezoid is usually considered to be a convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also crossed cases.
Trapezoid special cases.
.
The orange figures also qualify as parallelograms
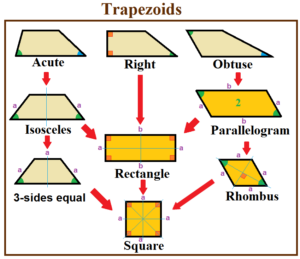
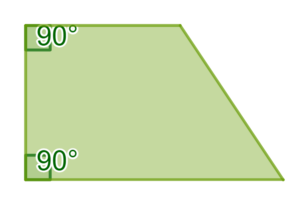 A right trapezoid (also called right-angled trapezoid) has two adjacent right angles.
A right trapezoid (also called right-angled trapezoid) has two adjacent right angles.  An acute trapezoid has two adjacent acute angles on its longer base edge.
An acute trapezoid has two adjacent acute angles on its longer base edge.
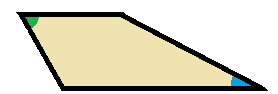 An obtuse trapezoid on the other hand has one acute and one obtuse angle on each base.
An obtuse trapezoid on the other hand has one acute and one obtuse angle on each base.
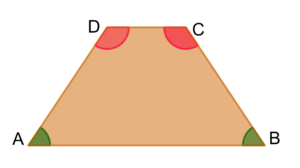
An isosceles trapezoid is a trapezoid where the base angles have the same measure and the legs are equal in length (AD = BC).
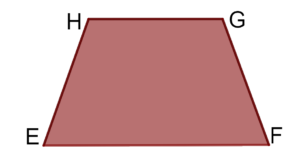 3-sides equal trapezoid is a trapezoid with three sides are equal (EH=HG=GF)
3-sides equal trapezoid is a trapezoid with three sides are equal (EH=HG=GF)
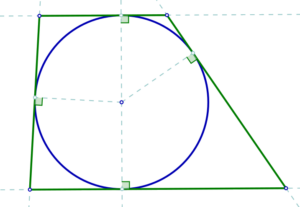 A tangential trapezoid is a trapezoid that has an incircle.
A tangential trapezoid is a trapezoid that has an incircle.
(Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trapezoid)
Midsegment, area, perimeter

The length of the midsegment of trapezoid is half the sum of the lengths of the two parallel sides.
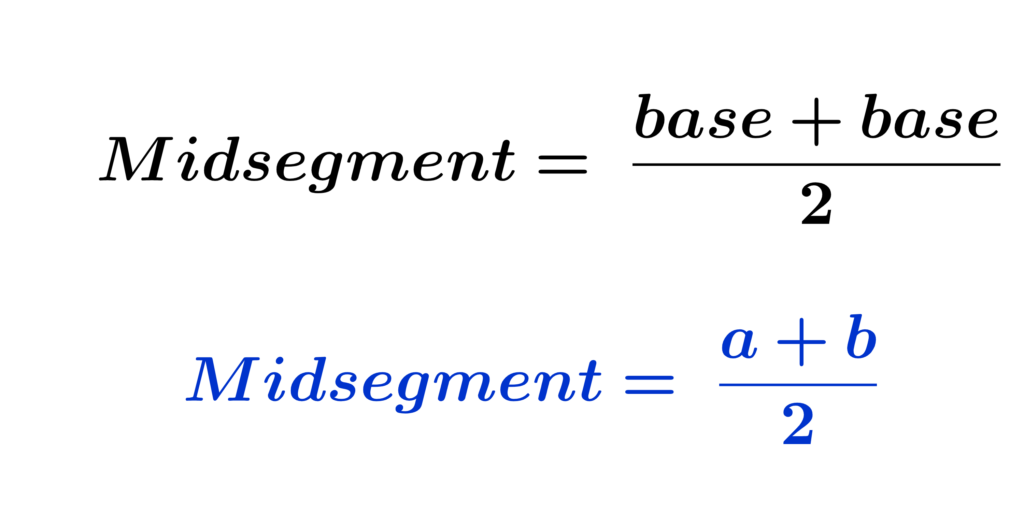
 a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides,
a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides,
h is the height (the perpendicular distance between these sides),
m is the (length of the midsegment) arithmetic mean of the lengths of the two parallel sides
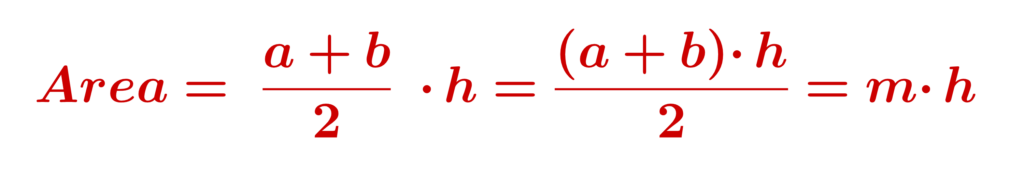
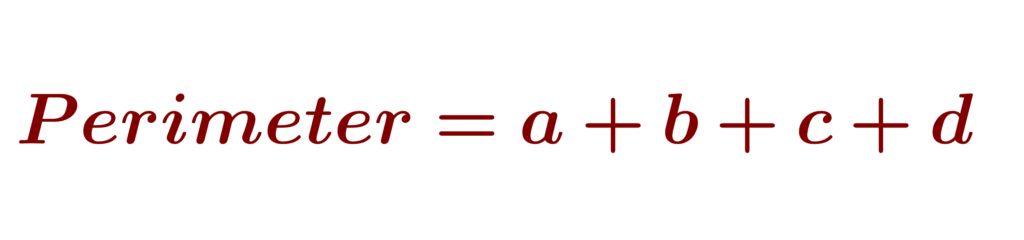
Tim Brzezinski , LicenseCC-BY-SA, GeoGebra Terms of Use
Tim Brzezinski , LicenseCC-BY-SA, GeoGebra Terms of Use
